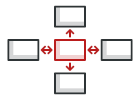
C++ 中介者模式讲解和代码示例
中介者是一种行为设计模式, 让程序组件通过特殊的中介者对象进行间接沟通, 达到减少组件之间依赖关系的目的。
中介者能使得程序更易于修改和扩展, 而且能更方便地对独立的组件进行复用, 因为它们不再依赖于很多其他的类。
复杂度:
流行度:
使用示例: 中介者模式在 C++ 代码中最常用于帮助程序 GUI 组件之间的通信。 在 MVC 模式中, 控制器是中介者的同义词。
概念示例
本例说明了中介者设计模式的结构并重点回答了下面的问题:
- 它由哪些类组成?
- 这些类扮演了哪些角色?
- 模式中的各个元素会以何种方式相互关联?
main.cc: 概念示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
/**
* The Mediator interface declares a method used by components to notify the
* mediator about various events. The Mediator may react to these events and
* pass the execution to other components.
*/
class BaseComponent;
class Mediator {
public:
virtual void Notify(BaseComponent *sender, std::string event) const = 0;
};
/**
* The Base Component provides the basic functionality of storing a mediator's
* instance inside component objects.
*/
class BaseComponent {
protected:
Mediator *mediator_;
public:
BaseComponent(Mediator *mediator = nullptr) : mediator_(mediator) {
}
void set_mediator(Mediator *mediator) {
this->mediator_ = mediator;
}
};
/**
* Concrete Components implement various functionality. They don't depend on
* other components. They also don't depend on any concrete mediator classes.
*/
class Component1 : public BaseComponent {
public:
void DoA() {
std::cout << "Component 1 does A.\n";
this->mediator_->Notify(this, "A");
}
void DoB() {
std::cout << "Component 1 does B.\n";
this->mediator_->Notify(this, "B");
}
};
class Component2 : public BaseComponent {
public:
void DoC() {
std::cout << "Component 2 does C.\n";
this->mediator_->Notify(this, "C");
}
void DoD() {
std::cout << "Component 2 does D.\n";
this->mediator_->Notify(this, "D");
}
};
/**
* Concrete Mediators implement cooperative behavior by coordinating several
* components.
*/
class ConcreteMediator : public Mediator {
private:
Component1 *component1_;
Component2 *component2_;
public:
ConcreteMediator(Component1 *c1, Component2 *c2) : component1_(c1), component2_(c2) {
this->component1_->set_mediator(this);
this->component2_->set_mediator(this);
}
void Notify(BaseComponent *sender, std::string event) const override {
if (event == "A") {
std::cout << "Mediator reacts on A and triggers following operations:\n";
this->component2_->DoC();
}
if (event == "D") {
std::cout << "Mediator reacts on D and triggers following operations:\n";
this->component1_->DoB();
this->component2_->DoC();
}
}
};
/**
* The client code.
*/
void ClientCode() {
Component1 *c1 = new Component1;
Component2 *c2 = new Component2;
ConcreteMediator *mediator = new ConcreteMediator(c1, c2);
std::cout << "Client triggers operation A.\n";
c1->DoA();
std::cout << "\n";
std::cout << "Client triggers operation D.\n";
c2->DoD();
delete c1;
delete c2;
delete mediator;
}
int main() {
ClientCode();
return 0;
}
Output.txt: 执行结果
Client triggers operation A.
Component 1 does A.
Mediator reacts on A and triggers following operations:
Component 2 does C.
Client triggers operation D.
Component 2 does D.
Mediator reacts on D and triggers following operations:
Component 1 does B.
Component 2 does C.