Java 享元模式讲解和代码示例
享元是一种结构型设计模式, 它允许你在消耗少量内存的情况下支持大量对象。
模式通过共享多个对象的部分状态来实现上述功能。 换句话来说, 享元会将不同对象的相同数据进行缓存以节省内存。
复杂度:
流行度:
使用示例: 享元模式只有一个目的: 将内存消耗最小化。 如果你的程序没有遇到内存容量不足的问题, 则可以暂时忽略该模式。
享元模式在核心 Java 程序库中的示例:
识别方法: 享元可以通过构建方法来识别, 它会返回缓存对象而不是创建新的对象。
渲染一片森林
本例中, 我们将渲染一片森林 (1,000,000 棵树)! 每棵树都由包含一些状态的对象来表示 (坐标和纹理等)。 尽管程序能够完成其主要工作, 但很显然它需要消耗大量内存。
原因很简单: 太多树对象包含重复数据 (名称、 纹理和颜色)。 因此我们可用享元模式来将这些数值存储在单独的享元对象中 ( TreeType类)。 现在我们不再将相同数据存储在数千个 Tree对象中, 而是使用一组特殊的数值来引用其中一个享元对象。
客户端代码不会知道任何事情, 因为重用享元对象的复杂机制隐藏在了享元工厂中。
trees
trees/Tree.java: 包含每棵树的独特状态
package refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.trees;
import java.awt.*;
public class Tree {
private int x;
private int y;
private TreeType type;
public Tree(int x, int y, TreeType type) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.type = type;
}
public void draw(Graphics g) {
type.draw(g, x, y);
}
}
trees/TreeType.java: 包含多棵树共享的状态
package refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.trees;
import java.awt.*;
public class TreeType {
private String name;
private Color color;
private String otherTreeData;
public TreeType(String name, Color color, String otherTreeData) {
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
this.otherTreeData = otherTreeData;
}
public void draw(Graphics g, int x, int y) {
g.setColor(Color.BLACK);
g.fillRect(x - 1, y, 3, 5);
g.setColor(color);
g.fillOval(x - 5, y - 10, 10, 10);
}
}
trees/TreeFactory.java: 封装创建享元的复杂机制
package refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.trees;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TreeFactory {
static Map<String, TreeType> treeTypes = new HashMap<>();
public static TreeType getTreeType(String name, Color color, String otherTreeData) {
TreeType result = treeTypes.get(name);
if (result == null) {
result = new TreeType(name, color, otherTreeData);
treeTypes.put(name, result);
}
return result;
}
}
forest
forest/Forest.java: 我们绘制的森林
package refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.forest;
import refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.trees.Tree;
import refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.trees.TreeFactory;
import refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.trees.TreeType;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Forest extends JFrame {
private List<Tree> trees = new ArrayList<>();
public void plantTree(int x, int y, String name, Color color, String otherTreeData) {
TreeType type = TreeFactory.getTreeType(name, color, otherTreeData);
Tree tree = new Tree(x, y, type);
trees.add(tree);
}
@Override
public void paint(Graphics graphics) {
for (Tree tree : trees) {
tree.draw(graphics);
}
}
}
Demo.java: 客户端代码
package refactoring_guru.flyweight.example;
import refactoring_guru.flyweight.example.forest.Forest;
import java.awt.*;
public class Demo {
static int CANVAS_SIZE = 500;
static int TREES_TO_DRAW = 1000000;
static int TREE_TYPES = 2;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Forest forest = new Forest();
for (int i = 0; i < Math.floor(TREES_TO_DRAW / TREE_TYPES); i++) {
forest.plantTree(random(0, CANVAS_SIZE), random(0, CANVAS_SIZE),
"Summer Oak", Color.GREEN, "Oak texture stub");
forest.plantTree(random(0, CANVAS_SIZE), random(0, CANVAS_SIZE),
"Autumn Oak", Color.ORANGE, "Autumn Oak texture stub");
}
forest.setSize(CANVAS_SIZE, CANVAS_SIZE);
forest.setVisible(true);
System.out.println(TREES_TO_DRAW + " trees drawn");
System.out.println("---------------------");
System.out.println("Memory usage:");
System.out.println("Tree size (8 bytes) * " + TREES_TO_DRAW);
System.out.println("+ TreeTypes size (~30 bytes) * " + TREE_TYPES + "");
System.out.println("---------------------");
System.out.println("Total: " + ((TREES_TO_DRAW * 8 + TREE_TYPES * 30) / 1024 / 1024) +
"MB (instead of " + ((TREES_TO_DRAW * 38) / 1024 / 1024) + "MB)");
}
private static int random(int min, int max) {
return min + (int) (Math.random() * ((max - min) + 1));
}
}
OutputDemo.png: 屏幕截图
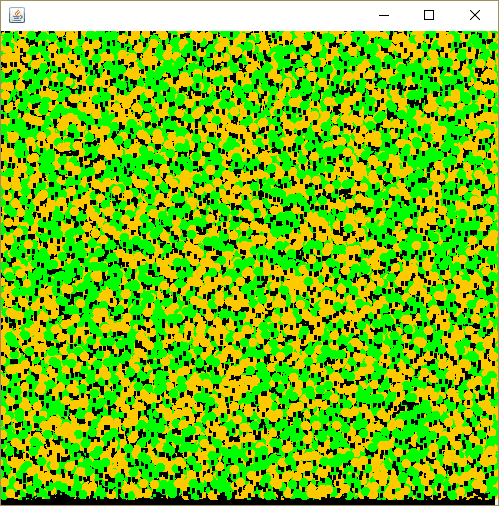
OutputDemo.txt: 内存使用统计
1000000 trees drawn
---------------------
Memory usage:
Tree size (8 bytes) * 1000000
+ TreeTypes size (~30 bytes) * 2
---------------------
Total: 7MB (instead of 36MB)